9. Complex Numbers and Trigonometry#
9.1. Overview#
This lecture introduces some elementary mathematics and trigonometry.
Useful and interesting in its own right, these concepts reap substantial rewards when studying dynamics generated by linear difference equations or linear differential equations.
For example, these tools are keys to understanding outcomes attained by Paul Samuelson (1939) [Samuelson, 1939] in his classic paper on interactions between the investment accelerator and the Keynesian consumption function, our topic in the lecture Samuelson Multiplier Accelerator.
In addition to providing foundations for Samuelson’s work and extensions of it, this lecture can be read as a stand-alone quick reminder of key results from elementary high school trigonometry.
So let’s dive in.
9.1.1. Complex Numbers#
A complex number has a real part and a purely imaginary part .
The Euclidean, polar, and trigonometric forms of a complex number are:
The second equality above is known as Euler’s formula
Euler contributed many other formulas too!
The complex conjugate of is defined as
The value is the real part of and is the imaginary part of .
The symbol = represents the modulus of .
The value is the Euclidean distance of vector from the origin:
The value is the angle of with respect to the real axis.
Evidently, the tangent of is .
Therefore,
Three elementary trigonometric functions are
We’ll need the following imports:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (11, 5) #set default figure size
import numpy as np
from sympy import (Symbol, symbols, Eq, nsolve, sqrt, cos, sin, simplify,
init_printing, integrate)
9.1.2. An Example#
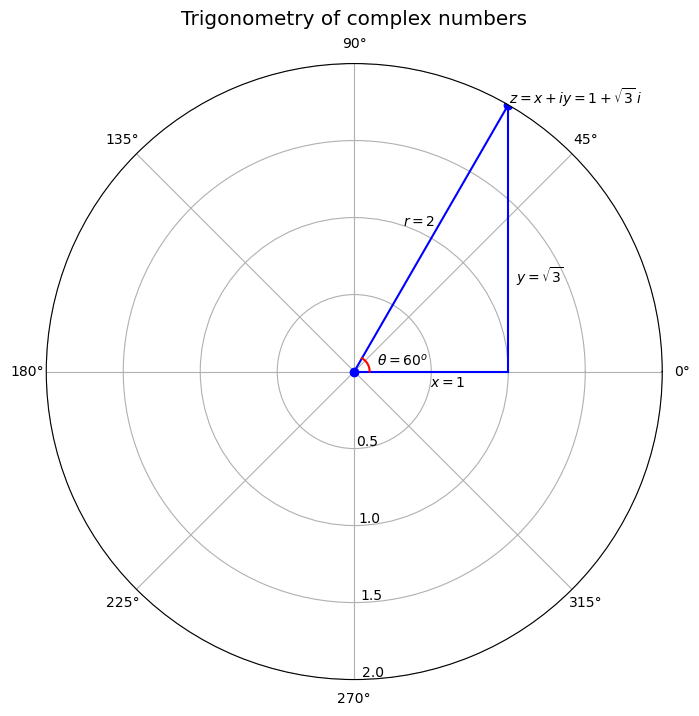
Example 9.1
Consider the complex number .
For , , .
It follows that and .
Let’s use Python to plot the trigonometric form of the complex number .
# Abbreviate useful values and functions
π = np.pi
# Set parameters
r = 2
θ = π/3
x = r * np.cos(θ)
x_range = np.linspace(0, x, 1000)
θ_range = np.linspace(0, θ, 1000)
# Plot
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
ax = plt.subplot(111, projection='polar')
ax.plot((0, θ), (0, r), marker='o', color='b') # Plot r
ax.plot(np.zeros(x_range.shape), x_range, color='b') # Plot x
ax.plot(θ_range, x / np.cos(θ_range), color='b') # Plot y
ax.plot(θ_range, np.full(θ_range.shape, 0.1), color='r') # Plot θ
ax.margins(0) # Let the plot starts at origin
ax.set_title("Trigonometry of complex numbers", va='bottom',
fontsize='x-large')
ax.set_rmax(2)
ax.set_rticks((0.5, 1, 1.5, 2)) # Less radial ticks
ax.set_rlabel_position(-88.5) # Get radial labels away from plotted line
ax.text(θ, r+0.01 , r'$z = x + iy = 1 + \sqrt{3}\, i$') # Label z
ax.text(θ+0.2, 1 , '$r = 2$') # Label r
ax.text(0-0.2, 0.5, '$x = 1$') # Label x
ax.text(0.5, 1.2, r'$y = \sqrt{3}$') # Label y
ax.text(0.25, 0.15, r'$\theta = 60^o$') # Label θ
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()
9.2. De Moivre’s Theorem#
de Moivre’s theorem states that:
To prove de Moivre’s theorem, note that
and compute.
9.3. Applications of de Moivre’s Theorem#
9.3.1. Example 1#
We can use de Moivre’s theorem to show that .
We have
and thus
We recognize this as a theorem of Pythagoras.
9.3.2. Example 2#
Let and so that is the complex conjugate of .
form a complex conjugate pair of complex numbers.
Let and be another complex conjugate pair.
For each element of a sequence of integers .
To do so, we can apply de Moivre’s formula.
Thus,
9.3.3. Example 3#
This example provides machinery that is at the heard of Samuelson’s analysis of his multiplier-accelerator model [Samuelson, 1939].
Thus, consider a second-order linear difference equation
whose characteristic polynomial is
or
has roots .
A solution is a sequence that satisfies the difference equation.
Under the following circumstances, we can apply our example 2 formula to solve the difference equation
the roots of the characteristic polynomial of the difference equation form a complex conjugate pair
the values are given initial conditions
To solve the difference equation, recall from example 2 that
where are coefficients to be determined from information encoded in the initial conditions .
Since and the ratio of to is
We can solve this equation for then solve for using .
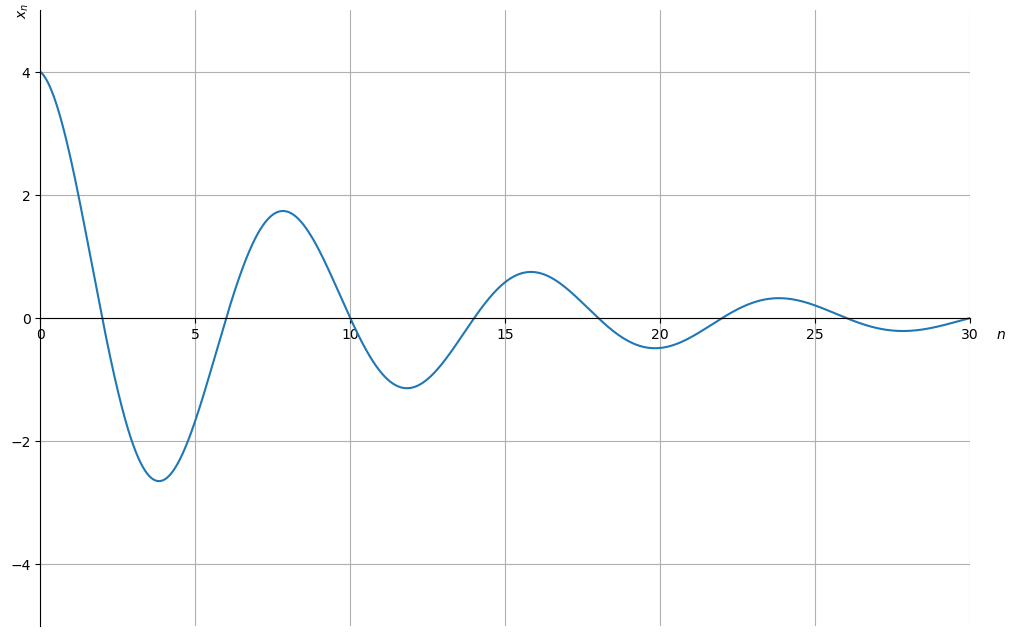
With the sympy package in Python, we are able to solve and plot the
dynamics of given different values of .
In this example, we set the initial values: - - - - .
We first numerically solve for and using
nsolve in the sympy package based on the above initial
condition:
# Set parameters
r = 0.9
θ = π/4
x0 = 4
x1 = 2 * r * sqrt(2)
# Define symbols to be calculated
ω, p = symbols('ω p', real=True)
# Solve for ω
## Note: we choose the solution near 0
eq1 = Eq(x1/x0 - r * cos(ω+θ) / cos(ω), 0)
ω = nsolve(eq1, ω, 0)
ω = float(ω)
print(f'ω = {ω:1.3f}')
# Solve for p
eq2 = Eq(x0 - 2 * p * cos(ω), 0)
p = nsolve(eq2, p, 0)
p = float(p)
print(f'p = {p:1.3f}')
ω = 0.000
p = 2.000
Using the code above, we compute that and .
Then we plug in the values we solve for and and plot the dynamic.
# Define range of n
max_n = 30
n = np.arange(0, max_n+1, 0.01)
# Define x_n
x = lambda n: 2 * p * r**n * np.cos(ω + n * θ)
# Plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))
ax.plot(n, x(n))
ax.set(xlim=(0, max_n), ylim=(-5, 5), xlabel='$n$', ylabel='$x_n$')
# Set x-axis in the middle of the plot
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position('center')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left')
ticklab = ax.xaxis.get_ticklabels()[0] # Set x-label position
trans = ticklab.get_transform()
ax.xaxis.set_label_coords(31, 0, transform=trans)
ticklab = ax.yaxis.get_ticklabels()[0] # Set y-label position
trans = ticklab.get_transform()
ax.yaxis.set_label_coords(0, 5, transform=trans)
ax.grid()
plt.show()
9.3.4. Trigonometric Identities#
We can obtain a complete suite of trigonometric identities by appropriately manipulating polar forms of complex numbers.
We’ll get many of them by deducing implications of the equality
For example, we’ll calculate identities for
and .
Using the sine and cosine formulas presented at the beginning of this lecture, we have:
We can also obtain the trigonometric identities as follows:
Since both real and imaginary parts of the above formula should be equal, we get:
The equations above are also known as the angle sum identities. We
can verify the equations using the simplify function in the
sympy package:
# Define symbols
ω, θ = symbols('ω θ', real=True)
# Verify
print("cos(ω)cos(θ) - sin(ω)sin(θ) =",
simplify(cos(ω)*cos(θ) - sin(ω) * sin(θ)))
print("cos(ω)sin(θ) + sin(ω)cos(θ) =",
simplify(cos(ω)*sin(θ) + sin(ω) * cos(θ)))
cos(ω)cos(θ) - sin(ω)sin(θ) = cos(θ + ω)
cos(ω)sin(θ) + sin(ω)cos(θ) = sin(θ + ω)
9.3.5. Trigonometric Integrals#
We can also compute the trigonometric integrals using polar forms of complex numbers.
For example, we want to solve the following integral:
Using Euler’s formula, we have:
and thus:
We can verify the analytical as well as numerical results using
integrate in the sympy package:
# Set initial printing
init_printing(use_latex="mathjax")
ω = Symbol('ω')
print('The analytical solution for integral of cos(ω)sin(ω) is:')
integrate(cos(ω) * sin(ω), ω)
The analytical solution for integral of cos(ω)sin(ω) is:
print('The numerical solution for the integral of cos(ω)sin(ω) \
from -π to π is:')
integrate(cos(ω) * sin(ω), (ω, -π, π))
The numerical solution for the integral of cos(ω)sin(ω) from -π to π is:
9.3.6. Exercises#
Exercise 9.1
We invite the reader to verify analytically and with the sympy package the following two equalities:
Solution to Exercise 9.1
Let’s import symbolic from sympy
# Import symbolic π from sympy
from sympy import pi
print('The analytical solution for the integral of cos(ω)**2 \
from -π to π is:')
integrate(cos(ω)**2, (ω, -pi, pi))
The analytical solution for the integral of cos(ω)**2 from -π to π is:
print('The analytical solution for the integral of sin(ω)**2 \
from -π to π is:')
integrate(sin(ω)**2, (ω, -pi, pi))
The analytical solution for the integral of sin(ω)**2 from -π to π is: